What is an Ad Server? An ad server is a technology which manages, serves, tracks and reports online display advertising campaigns. There are two types of ad servers in the advertising ecosystem: publisher (supply side) and advertiser (demand/buy side) ad server. Why should...
What is an Ad Server?
An ad server is a technology which manages, serves, tracks and reports online display advertising campaigns. There are two types of ad servers in the advertising ecosystem: publisher (supply side) and advertiser (demand/buy side) ad server.
Why should advertisers use ad servers to run campaigns? As an advertiser, what key factors should you look for when choosing an ad server for advertisers?
In a typical campaign, an advertiser would purchase ad inventories from different sources; websites & applications, including from programmatic platforms such as ad networks, DSPs and ad exchanges.
This becomes increasingly complex, as you would have to deal with multiple parties for tracking, creative changes and reporting.
To ensure efficiency in ad operations, advertisers use a third-party ad server to manage their campaigns. Their ads are uploaded to the ad server and then served into multiple traffic sources – using just a single ad tag script.
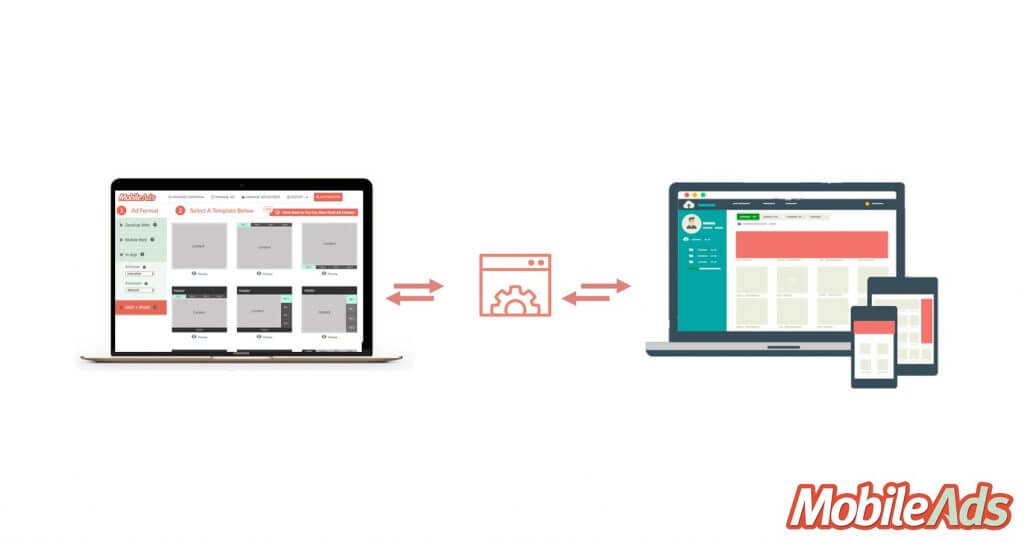 Illustrates the ad serving relationship between a publisher and ad server.
Illustrates the ad serving relationship between a publisher and ad server.
How do ad servers work?
While the process of ad serving happens within a few microseconds, many advertisers are still unclear on how it operates. Here’s a quick summary of the process:
1. When a user visits a page, the ad server of the publisher gets a request to display the ad.
2. Once the ad servers receive the request, it examines the data to choose the most appropriate ad for the viewer. The ad tag contains an extensive list of criteria fed by the advertiser. The ads will be selected based on several factors such as age, geography, size, behavior, etc.
3. Once the best matching ads are chosen, it will be shown to the user.
4. The ad gathers all information relating to the user interaction with the ad such as clicks, impressions, conversions, etc. The data is then carefully stored for the marketing team to analyze.
Difference between an ad server for advertisers and for publishers
As explained, ad servers were created to provide convenience, transparency, and efficiency in ad operations. However, there’s a confusion as to why an advertiser and publisher both have their own ad server?
The main reason is that at the end of the campaign, both the advertiser and publisher can cross-audit the campaign and manage billings accordingly following the ad impressions served, ad viewability, and performance.
Ad servers can be used as first-party (by publishers) and third party (by advertisers). While they are used for different purposes by both, they essentially use the same technology.
Here is a quick difference between both the types of ad servers:
What is an advertiser-side ad server?
An advertiser ad server (also known as third party ad servers) is used by advertisers (and media buyers) to show ads on different websites and apps. They allow advertisers to make creative changes that would be reflected in every site/app the ad tag is placed on.
It also acts as a single dashboard for campaign management and detailed reporting, for advertisers to manage ads and transparently track ad metrics such as viewability. Most advertiser ad servers have near real-time reporting capabilities, enabling advertisers to constantly optimize their ad campaigns.
What is a publisher-side ad server
A publisher ad server (also known as first party ad servers) is used by publishers to display & manage ads on their website or app. Besides detailed tracking, it allows the publisher to make certain rules, for example; which ads should show in particular sections of the website and to whom the ads should be shown to.
It can therefore be said that first party ad servers are used for targeting and making decisions regarding which ads to display on the website based on different factors. These could include parameters that are involved in serving the ads, collecting the data, measurements using impressions, clicks, etc.
Inventory forecasting based on current campaigns and future traffic projections is another important utility of first party ad servers.
Some publisher ad servers also come with a self-serve native ad creator, allowing publishers to create and manage special ad formats that follow the look and feel of their website or app.

Examples of native ad formats for publishers.
How does an ad server work?
In the early years of online advertising, ad buying and selling (between publishers and advertisers) was a manual process. Needless to say, it was required to come up with something which made the process easier and more efficient for publishers.
Following diagram explains the basics of ad serving process:
This led to the birth of first party or publisher ad servers.
Learn about the working of a publisher ad server (first party ad servers) and the advertiser’s ad server (third party ad server) in our follow up articles:
What is a Third Party Ad Server? What are the advantages of using a Third Party Ad Server? What are First Party Ad Servers (Publisher Ad Servers)? Mobile Ad Serving Best Ad Servers for Advertisers and Publishers What is a Third Party Ad Tag?Factors that make a good ad server.
Supports multiple ad formats & ad platform-agnostic
It is challenging to create ads compatible with the many different screen sizes, channels and platforms involved in a media buy campaign.
Ad servers take care of platform compatibility. Whether you are serving ads into a website or a mobile application, it ensures your ads load fast and correctly.
Image ads are compressed & turned into fast loading ad creatives. Video ads are automatically converted into ready ad-serving formats like VAST and VPAID. Ad servers also ensure elements on advanced ads such as HTML5 and rich media to be properly tracked and work on different platforms using industry standards such as MRAID.
Most ad inventory sources have in-built ad servers to serve static image ads, however, advance HTML5 and rich media creatives are still uncommon for them. Therefore, a good 3rd party ad server will have capabilities to serve and especially, track in-banner engagements of the ads.
At the same time, advertiser ad servers act as an independent auditor to check on the quality of ad inventory in the campaign. If advertisers use the server supplied by the inventory source (ad network, exchange, DSP, etc), there is no proper “check and balance” on the quality and quantity of ad placements. How would advertisers verify that the committed amount of views are actually served by the source?
A good advertiser-side ad server must also be certified in major traffic platforms, such as Google Marketing Platform, Google Display Network, MediaMath DSP and more. Otherwise, large ad campaigns that require media buying in major ad sources will be hindered by the coverage of the server’s certified ad platforms.
Real-time independent analytics & reporting
Ad servers must have close to real-time tracking & reporting features. This is important because you have to constantly optimize ad creatives and traffic quality to ensure a successful ad campaign. Instead of relying on the many account managers from different traffic sources to manually provide you with reports, with an ad server, you would be able to track and audit your ad campaigns in near real-time.
This enables you to make quick ‘on-the-fly’ optimization, avoiding ad budget losses.At the same time, advertisers will have a central dashboard that consolidates analytics of all different ad inventory sources into one and making campaign management much streamlined.
Ad creative A/B split-test capability
Part of the job of an ad server is to enable creative split-testing where you can upload a few ad creatives and track the winning creative that performs best.
You do this easily by using a single ad tag, which is embedded in all traffic sources. A single creative change on the ad server will automatically reflect on every traffic source.
So rather than having to manually recontact every account manager from different inventory sources, optimization can be quickly done from the ad server’s end.
Dynamic Creative Optimization (DCO)

In a digital world filled with ads, users are bombarded by hundreds of different ads every day. Reach is no longer an issue, but personalization is.
Making your ads relevant to the viewer through personalization is key to effective ad campaigns.
Dynamic Creative Optimization (DCO) is a method where you serve dynamic ads that stitch themselves in milliseconds, depending on who sees it, when and where it is served. For instance, if the viewer sees the ad in the morning, the ad creative could be made to show a time or weather sensitive headline, providing better relevance.
It works by having data from the traffic sources fed into the ad server. This happens in milliseconds and the creatives will automatically assemble accordingly, as they get shown to the viewer.
Some data that can be fed into the server includes:
– Location (country, state, etc)
– Time of day (afternoon, night, etc)
– Day of week
– Language
– Device (desktop, mobile, iPad, etc)
– Weather (cloudy, raining, etc)
Independent viewability audit of ad placements
It is reported by Google that up to 56.1% of ads served are not seen. This causes advertisers to lose ad budgets to non-viewable inventories.
With no transparency into whether your ads are loaded correctly or actually been seen, you’re left in the dark. This also brings to concern about ad fraud. Are your traffic sources even reporting real ad tracking metrics?
When running a display ad campaign, it’s important to have an ad viewability tracking tool existing as part of your campaign. Ad servers normally provide an internal ad viewability tracking tool to track ads. At the same time, when needed, it should also have an option to integrate third-party tracking tools.
Classification of Ad Servers based on Creatives
Ad servers are designed to handle different types of ad formats. Certain features such as the specific placement of ads may vary depending on the kind of ad servers.
Ad servers can be classified based on ad creatives in the following types:
1. Rich media ad servers
The rich media ad servers are designed to serve ads that contain multiple files such as audios, images, and videos.
This is an advanced type of ad serving in which not all servers are supported. Detailed tracking of users’ interactions with the ad is also done. Some rich media ad servers offer templates that can be placed directly on the webpage instead of coding the complex script by yourself.
2. Display ad servers
These are the oldest and simplest forms of advertising on the web. Display ad servers are designed to handle different forms of banner ads.
Here you could run advertising campaigns as well as manage the placement of banner ad creatives. Some of its features include:
Affordable and easy to track. Ad placement is possible anywhere on the website. Gives your maximum ad exposure.Disadvantages:
Banner blindness-where the viewer subconsciously tends to ignore the presence of the ad. Low CTR3. Mobile ad servers
Mobile advertising is not different from desktop advertising, except that the size has to be minimized. Most display ad servers support mobile advertising.
These ad servers are suited for mobile advertising on in-app monetization. For in-app advertising SDK kit has to be embedded in the app to connect with the ad servers.
4. Video ad servers
Just like the name suggests these are specifically suited to serve video ads, both instream, and outstream. The great thing about video advertising is that it has 7.5 times higher CTR than the standard banner ads.
While the out-stream video can be displayed anywhere on the page as the advertiser pleases, instream ads require the publisher to have a video player on their website.
Video ad serving is a lot more complicated than other forms of advertising. Videos should comply with IAB standards such as VMAP, VPAID or VAST.
5. Native ad servers
The Native ads are designed to naturally blend with regular web content, which is why several ad networks favour this format.
In short native ad servers are designed to serve the ads that will naturally go along with the publisher’s website’s regular content.
Advanced ad servers like Epom can integrate ad placement into their CMS system. They also provide a native template adapter to adjust the creative to suit a particular website.
Are you an advertiser looking to serve ads into multiple ad inventories and publishers? Request a demo at MobileAds and learn how to manage your campaign more efficiently.











