Unlock the potential of large vision models in AI. Discover how SoluLab can help your business thrive in age of intelligent vision systems. The post A Brief Guide to Large Vision Models appeared first on Blockchain Technology, Mobility, AI...
In the era of rapid technological evolution, the transformative power of artificial intelligence (AI) has taken center stage, with large vision models emerging as pioneers in reshaping various industries. These advanced AI systems, meticulously designed for deciphering and interpreting visual data, are at the forefront of a paradigm shift, ushering in a new era of efficiency, precision, and innovation.
Our blog aims to delve into the realm of large vision models, providing a comprehensive exploration of their definition, significance, and the profound influence they exert across diverse sectors. As we embark on this journey, we’ll unravel the intricacies of these sophisticated neural networks, emphasizing their vast scale and intricate architectures.
From healthcare to manufacturing, finance to entertainment, large vision models have become indispensable assets, driving unprecedented advancements in decision-making, automation, and problem-solving. The intricate dance between technology and real-world applications is reshaping how we perceive and interact with the world around us.
Join us as we navigate through the multifaceted landscape of large vision models, uncovering their pivotal role in revolutionizing industries and gaining insights into the limitless possibilities they unlock. As we peer into the future, it becomes clear that the impact of these intelligent systems extends far beyond mere automation – they are catalysts for innovation, efficiency, and a future where the synergy between artificial intelligence and human ingenuity knows no bounds.
What are Large Vision Models?
Large vision models refer to advanced artificial intelligence (AI) systems specifically designed for processing and interpreting visual information. These models are typically based on deep learning architectures and are trained on vast datasets to acquire the ability to understand and analyze visual data. The term “large” emphasizes the substantial size and complexity of these models, often measured in terms of the number of parameters.
These models are a subset of the broader category of artificial neural networks and are specifically tailored to excel at tasks related to computer vision. Computer vision involves the use of AI to enable machines to interpret and make decisions based on visual data, such as images and videos.
Use Cases in Various Industries
Large vision models use cases for transformative change across a spectrum of industries, each reaping unique benefits from the advanced capabilities these models bring to the table.
Healthcare
Large vision models are revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy through image analysis. From identifying anomalies in medical imaging to predicting disease progression, these models assist healthcare professionals in making informed decisions, leading to improved patient outcomes and personalized treatment plans.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, large vision models play a pivotal role in enabling autonomous vehicles. These models process vast amounts of visual data from sensors, ensuring precise navigation, object recognition, and real-time decision-making. This not only enhances road safety but also propels the automotive industry into the future of smart and self-driving vehicles.
Manufacturing
Large vision models are employed in manufacturing for quality control and optimization. They can swiftly detect defects in production lines, ensuring the delivery of high-quality products. Additionally, these models contribute to process efficiency by monitoring and analyzing visual data, leading to streamlined manufacturing processes.
Retail
Retailers leverage large vision models for customer analytics, enabling personalized marketing strategies. These models analyze customer behavior, preferences, and demographics from visual data, facilitating targeted advertising and improving the overall shopping experience. Inventory management also benefits from these models, ensuring optimal stock levels and reducing losses.
Finance
In the financial sector, large vision models are instrumental in fraud detection. They analyze patterns and anomalies in visual data, identifying suspicious activities and mitigating risks. Moreover, these models streamline document processing, automating tasks such as document verification and data extraction, and enhancing operational efficiency.
Entertainment
Large vision models are reshaping the entertainment industry by powering content recommendation systems. By analyzing user interactions with visual content, these models personalize recommendations, keeping audiences engaged. They also contribute to video and image editing automation, bringing efficiency to content creation processes.
Security and Surveillance
Enhanced security and surveillance owe much to large vision models. These models excel in object detection and tracking, bolstering security measures in public spaces and critical infrastructure. Their ability to detect anomalies aids in proactive threat prevention, making them indispensable in safeguarding communities.
Agriculture
Agriculture benefits from large vision models through precision farming. These models analyze visual data from drones and satellites to monitor crop health, predict yields, and identify potential issues like pests or diseases. This data-driven approach optimizes agricultural practices, improving crop yields and sustainability.
Education
The education sector utilizes large vision models for automated grading and assessment of visual content. These models analyze student responses, providing timely and objective feedback. Customized learning experiences are facilitated through adaptive learning platforms that tailor content based on individual student interactions, fostering a more personalized education journey.
In essence, the importance of large vision models in various industries lies in their capacity to elevate efficiency, accuracy, and innovation, thereby reshaping the way businesses operate and deliver value in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Examples of Large Vision Models (LVMs)
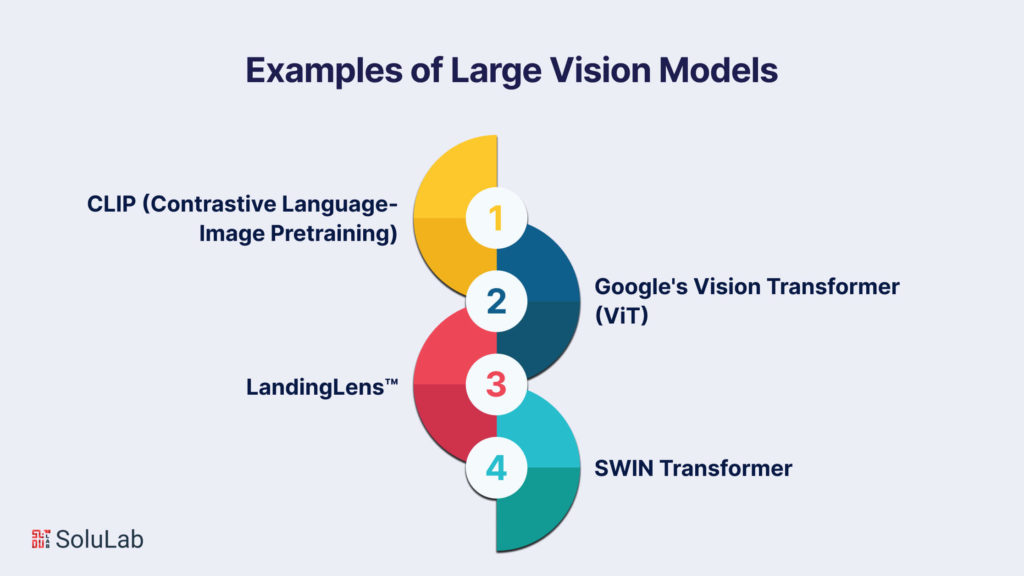
Explore a glimpse into the realm of Large Vision Models (LVMs) and their diverse capabilities:
CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining): Developed by OpenAI, CLIP represents a groundbreaking vision-language model meticulously trained to comprehend images in tandem with natural language. This sophisticated model finds applications in image captioning, visual question answering, and image retrieval. Google’s Vision Transformer (ViT): Referred to as ViT, Google’s Vision Transformer is tailored for image classification, employing a unique Transformer-like architecture that operates on patches of the image. ViT has garnered acclaim for achieving state-of-the-art results across various image classification benchmarks. LandingLens™: A revolutionary platform crafted by LandingAI, LandingLens™ democratizes computer vision projects by empowering users without prior coding experience. This intuitive platform offers a user-friendly interface for tasks such as image labeling, model training, and seamless deployment to both cloud and edge devices. SWIN Transformer: The SWIN Transformer presents a hierarchical design for visual recognition tasks. With success in image classification and object detection, SWIN utilizes hierarchical representations, showcasing its versatility in handling complex visual information.These examples underscore the diverse applications of Large Vision Models, showcasing their ability to bridge the gap between language and images, optimize image classification, and democratize computer vision projects for users across different expertise levels.
Distinctive Features of Large Vision Models: Parameters and Scale
Large vision models in AI stand out in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) due to their distinctive features, and among these, the sheer scale of parameters is a key distinguishing factor. As we delve into this aspect, it becomes evident that the size and complexity of these models contribute significantly to their effectiveness and versatility.
Parameters: The Driving Force Behind Large Vision Models
Unprecedented Scale: Large vision models are characterized by an immense number of parameters, surpassing the scale of their predecessors. These parameters are the internal variables that the model adjusts during training, enabling it to capture intricate patterns and nuances within visual data. Deep Architectures: These models often adopt deep neural network architectures, comprising multiple layers of interconnected nodes. The depth of these architectures allows the model to learn hierarchical representations, from simple features to more abstract and complex concepts, enabling a nuanced understanding of visual information. Learned Representations: The expansive parameter space allows large vision models to learn rich and diverse representations of visual data. This is especially crucial in tasks like image recognition, where the model can discern intricate details and subtle variations, leading to improved accuracy and robustness. Transfer Learning Capabilities: Large vision models excel in transfer learning, a technique where a pre-trained model on a massive dataset can be fine-tuned for specific tasks with relatively smaller datasets. This adaptability makes them versatile across various applications, from medical image analysis to industrial quality control.Scale: Beyond the Numbers
Massive Datasets: Large vision models in AI thrive on extensive training datasets that encompass a vast array of visual information. The scale of these datasets contributes to the model’s ability to generalize well to diverse scenarios, ensuring robust performance in real-world applications. Computational Intensity: The training process for large vision models is computationally intensive, often requiring powerful hardware accelerators like GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) or TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). The scale of computation involved is a testament to the complexity of the models and the depth of the learning they undergo. Real-Time Inference Challenges: While the training phase benefits from ample computational resources, the scale of these models poses challenges during real-time inference, especially in resource-constrained environments. Optimizing for deployment on edge devices becomes a critical consideration. Interconnectedness of Parameters: The intricate web of parameters in large vision models contributes to their interconnectedness. This interconnected nature allows the model to grasp complex relationships within visual data, facilitating tasks such as object detection, segmentation, and image understanding.In summary, the distinctive features of large vision models, particularly their scale and parameters, showcase the strides made in the field of AI. These models, characterized by their vast parameter space and computational demands, embody the pinnacle of current technological capabilities, enabling them to excel in understanding and interpreting visual information with unprecedented accuracy and depth.
Key Capabilities of Large Vision Models
Large vision models, distinguished by their expansive architectures and sophisticated training, possess a diverse set of capabilities that extend far beyond simple image analysis. Let’s explore the key functionalities that make these models integral components of AI advancements.
Image Recognition
Large vision models in AI excel in the realm of image recognition, demonstrating a remarkable ability to identify and classify objects within visual data. Through their extensive training on massive datasets, these models can recognize patterns, shapes, and features with a level of accuracy that transcends conventional image processing techniques.
Pattern Recognition: Large vision models can discern intricate patterns within images, enabling them to recognize objects with diverse shapes and structures. Contextual Understanding: The models leverage their extensive training to understand the contextual significance of objects, enhancing their capacity to recognize and classify entities within complex scenes.Object Detection
One of the standout capabilities of large vision models is their prowess in object detection. By breaking down images into constituent elements, these models can precisely locate and identify multiple objects within a given scene.
Bounding Box Prediction: Large vision models employ bounding boxes to precisely delineate the location of objects in an image, offering a detailed understanding of spatial relationships. Multi-Object Recognition: The models can simultaneously detect and classify multiple objects within a single image, making them invaluable in scenarios where diverse elements coexist.Image Captioning
Large vision models go beyond static image analysis by venturing into the realm of natural language understanding. Image captioning is a testament to their capacity to generate textual descriptions based on visual input.
Semantic Description: These models generate meaningful and contextually relevant descriptions, showcasing their understanding of the semantic content within images. Multimodal Fusion: The integration of visual and textual information demonstrates the models’ ability to fuse different modalities, paving the way for more comprehensive and human-like interactions.Visual Question Answering
The fusion of vision and language is a defining characteristic of large vision models, as evidenced by their capability to answer questions related to visual content.
Contextual Reasoning: Large vision models can infer answers by considering both the visual context and the textual question, showcasing their capacity for nuanced reasoning. Multimodal Understanding: The integration of vision and language enables these models to provide informative and relevant answers to a wide array of visual queries.Customization and Accessibility
Large vision models contribute to democratizing computer vision projects by offering customization options and user-friendly interfaces, making AI more accessible to individuals with varying levels of expertise.
User-Friendly Interfaces: Platforms like LandingLens™ provide intuitive interfaces that empower users, even those without coding experience, to create custom computer vision projects. Accessible Training: Large vision models facilitate the training of custom models, allowing users to tailor AI solutions to specific needs and applications, thereby expanding the accessibility of AI technology.In essence, the key capabilities of large vision models underscore their adaptability and multifaceted nature, positioning them as invaluable tools in solving complex problems across diverse domains in the ever-evolving landscape of AI.
Applications of Large Vision Models
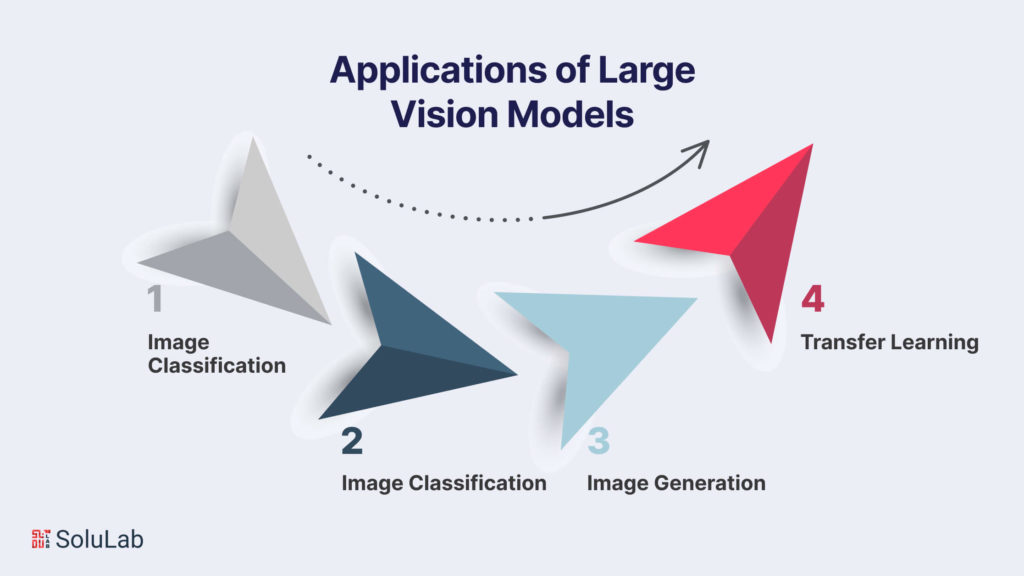
Large vision models use cases have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence, paving the way for a myriad of applications that span industries and domains. Their ability to comprehend and interpret visual information with remarkable accuracy has ushered in a new era of automation and innovation. Here, we delve into some of the key applications where these models are making a profound impact:
A. Image Classification
Image classification stands as one of the foundational applications of large vision models. These models, often based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), have demonstrated exceptional prowess in categorizing images across a vast spectrum. From identifying objects and scenes to recognizing complex patterns, image classification is employed in various sectors such as healthcare for medical image analysis, in manufacturing for quality control, and in e-commerce for visual search functionalities. Large vision models enable machines to emulate human-like visual perception, facilitating accurate and rapid decision-making based on visual input.
B. Object Detection
In the realm of object detection, large vision models showcase their versatility by precisely locating and delineating multiple objects within images or video streams. Applications of object detection are manifold and extend to fields like surveillance, where it enhances security through the identification of suspicious activities, and in autonomous vehicles, enabling them to navigate and interact with their surroundings. Retail industries leverage object detection for inventory management and the improvement of customer experiences through automated checkout processes.
C. Image Generation
The capability of large vision models in image generation has opened up creative possibilities in various domains. Generative AI models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), leverage the knowledge acquired from extensive datasets to create new, realistic images. This application finds use in the creative arts, design, and entertainment industries. From generating artwork to producing synthetic visual content, large vision models contribute to the creation of novel and visually appealing material.
D. Transfer Learning
Transfer learning represents a paradigm shift in the application of large vision models, allowing the transfer of knowledge gained from one task to another. By leveraging pre-trained models, often trained on massive datasets, developers can adapt these models for specific applications with limited labeled data. This versatility makes transfer learning a powerful tool across domains, from healthcare and finance to natural language processing. Large vision models, acting as knowledge repositories, expedite the development of tailored solutions by capitalizing on their pre-existing understanding of visual data.
In each of these applications, large vision models showcase their transformative potential, fundamentally altering how machines perceive and interact with the visual world. As these models continue to evolve, their impact on industries and daily life is poised to deepen, driving advancements in automation, decision support systems, and creative endeavors.
Challenges in Developing Large-Vision Models
The development of large vision models in AI has undoubtedly propelled the capabilities of artificial intelligence, but this progress is not without its set of challenges. Navigating these hurdles is crucial to harnessing the full potential of these sophisticated systems.
A. Computational Resources
Building and training large vision models in AI demand substantial computational resources. The sheer scale and complexity of these models, often comprising millions or even billions of parameters, necessitate robust hardware accelerators like Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) or specialized Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). Access to such high-performance computing infrastructure poses a significant challenge, especially for smaller organizations or researchers with limited resources. The computational demands extend not only to training but also to the deployment and inference phases, requiring ongoing investments in infrastructure.
B. Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns
The utilization of large vision models in AI raises critical data privacy and ethical concerns. Training these models involves massive datasets that may contain sensitive information. Ensuring the responsible and ethical use of such data is paramount. The risk of unintentionally incorporating biases present in the training data adds an additional layer of complexity. Striking a balance between leveraging diverse datasets for model improvement and safeguarding individual privacy requires robust data governance frameworks, ethical guidelines, and transparent practices throughout the model development lifecycle.
C. Bias and Fairness Issues
Bias and fairness issues represent a persistent challenge in the development of large vision models in AI. These models learn from diverse datasets, and if these datasets are not carefully curated, they may perpetuate and even exacerbate existing biases present in the data. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes in the model’s predictions or decisions. Mitigating bias and ensuring fairness necessitate a proactive approach, involving thorough examination and curation of training data, continual monitoring of model outputs, and the implementation of fairness-aware algorithms. Addressing bias is not only an ethical imperative but also crucial for building trust in AI systems.
In addressing these challenges associated with large vision models in AI, the field stands to achieve not only technical advancements but also the development of responsible, ethical, and unbiased AI systems. As these models continue to evolve, a holistic approach that considers both technological and ethical dimensions will be essential to unlock their full potential for positive societal impact.
Future Trends in Large Vision Models
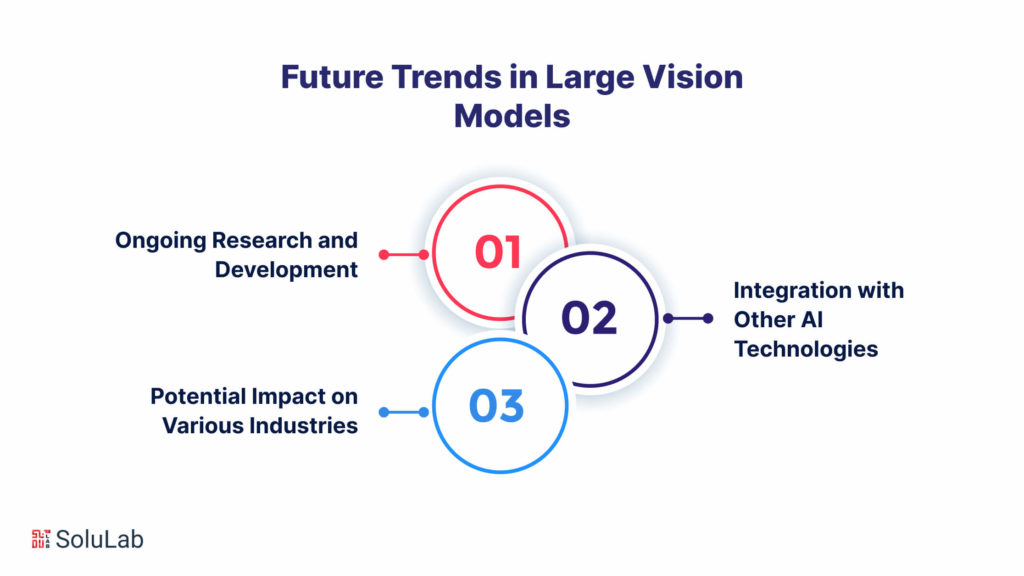
As we peer into the future, the trajectory of large vision models in AI holds promise for groundbreaking advancements, influencing not only the technical landscape but also reshaping the way industries operate.
A. Ongoing Research and Development
Ongoing research and developments in the realm of large vision models promise to push the boundaries of what’s achievable. Researchers are actively exploring novel architectures, optimization techniques, and training methodologies to enhance the efficiency and performance of these models. Continued efforts in addressing challenges such as model interpretability, reducing computational requirements, and developing more energy-efficient solutions are likely to drive the evolution of large vision models. The exploration of unsupervised and self-supervised learning methods is expected to broaden the applicability of these models across domains with limited labeled data.
B. Integration with Other AI Technologies
The integration of large vision models with other AI technologies is set to create synergies that amplify the overall capabilities of artificial intelligence. Collaborations between large vision models and natural language processing (NLP) models, for example, could lead to more comprehensive AI systems capable of understanding and generating both visual and textual information. Additionally, the fusion of large vision models with reinforcement learning techniques may pave the way for more advanced decision-making in dynamic and complex environments. The interdisciplinary integration of AI technologies holds the potential to create more versatile and context-aware systems.
C. Potential Impact on Various Industries
The potential impact of large vision models on various industries is poised to be transformative. In healthcare, these models may play a pivotal role in diagnostics, drug discovery, and personalized medicine, augmenting the capabilities of medical professionals. In manufacturing, large vision models could further enhance quality control processes, contributing to increased efficiency and reduced defects. The integration of these models in retail may revolutionize customer experiences through advanced recommendation systems and cashier-less checkout solutions. Moreover, the utilization of large vision models in autonomous vehicles could propel the development of safer and more reliable transportation systems.
The overarching theme is the democratization of AI capabilities across industries, empowering businesses and organizations to leverage large vision models for improved decision-making, automation, and innovation. The cross-pollination of ideas and technologies from ongoing research is likely to lead to solutions that are not only more powerful but also more accessible, driving a democratization of AI capabilities across industries. As large vision models continue to evolve, their seamless integration with other AI technologies and their positive impact on diverse sectors herald a future where AI becomes an integral part of our daily lives, making tasks smarter, more efficient, and increasingly tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the trajectory of large vision models in artificial intelligence is nothing short of remarkable. From redefining image classification to influencing the ethical dimensions of AI, these models have become pivotal players in the technological landscape. As we embrace the ongoing research, anticipate interdisciplinary collaborations, and foresee the transformative impact on various industries, it becomes evident that large vision models are not just a tool; they represent a paradigm shift in how we approach and leverage artificial intelligence.
As we stand on the cusp of this AI revolution, organizations aiming to harness the potential of large vision models need a strategic partner that understands the nuances of this rapidly evolving field. SoluLab, a well-known AI development company, with its expertise in great technologies, stands poised to assist businesses in navigating the complexities of large vision models. From conceptualizing and developing custom AI solutions to addressing ethical considerations and ensuring responsible AI deployment, SoluLab is committed to being at the forefront of this technological evolution. By combining innovative solutions with a client-centric approach, SoluLab empowers businesses to not only adopt large vision models seamlessly but also to stay ahead in the dynamic landscape of artificial intelligence.
FAQs
1. What distinguishes large vision models from traditional computer vision techniques?
Large vision models differ from traditional computer vision techniques in their scale and complexity. While traditional methods often rely on handcrafted features and algorithms, large vision models, such as deep neural networks, learn hierarchical representations directly from data, allowing them to capture intricate patterns and features.
2. How do large vision models handle bias in their predictions?
Addressing bias in large vision models is an ongoing challenge. To mitigate bias, careful curation of training data is essential, including the identification and removal of biased samples. Additionally, employing fairness-aware algorithms and conducting regular audits of model outputs can help identify and rectify biases, promoting more equitable predictions.
3. What are the computational requirements for training large vision models?
Training large vision models demands significant computational resources, often relying on high-performance hardware like GPUs or TPUs. The computational requirements can be a challenge for smaller organizations. Cloud-based solutions and distributed computing frameworks are commonly used to alleviate these challenges and make large-scale model training more accessible.
4. Can large vision models be applied to industries beyond healthcare and manufacturing?
Absolutely. Large vision models have versatile applications across various industries. From enhancing customer experiences in retail to optimizing logistics and decision-making in finance, the adaptability of these models allows them to play a transformative role in diverse sectors.
5. How can SoluLab assist businesses in adopting large vision models?
SoluLab is equipped to guide businesses through the adoption of large vision models. Our expertise encompasses custom AI solution development, addressing ethical considerations, and ensuring responsible AI deployment. With a client-centric approach, SoluLab empowers businesses to seamlessly integrate large vision models into their operations, staying at the forefront of AI advancements.
6. Are there any emerging trends in large vision models that businesses should watch for?
Yes, ongoing research is exploring novel architectures and integration with other AI technologies. Businesses should stay attentive to advancements in unsupervised learning, interdisciplinary collaborations, and applications in areas like natural language processing. SoluLab, with its commitment to staying ahead in technology, can help businesses leverage these emerging trends for strategic advantages.
The post A Brief Guide to Large Vision Models appeared first on Blockchain Technology, Mobility, AI and IoT Development Company USA, Canada.




