Linguistic Anthropology is the anthropological study of language. It includes 3 fields: Descriptive Linguistics, Historical Linguistics, and Sociolinguistics. Descriptive Linguistics involves describing languages and writing down spoken languages. Historical Linguistics looks at things like language variation and how language...
Linguistic Anthropology is the anthropological study of language. It includes 3 fields: Descriptive Linguistics, Historical Linguistics, and Sociolinguistics. Descriptive Linguistics involves describing languages and writing down spoken languages. Historical Linguistics looks at things like language variation and how language changes over time. And finally, Sociolinguistics studies the social and cultural context of language and looks at how language is affected by gender, class, age, and other factors. In a previous post, I focused on Historical Linguistics and talked about how language changes over time. In this post, I’d like to continue talking about Historical Linguistics and focus on how languages are related.
How Are Languages Related?
Languages are related to each other through language families. A language family is a group of languages that all descended from one ancestral language. For example, French, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, and Romanian are related, and they all developed from Latin. Latin is the protolanguage for these languages, meaning it was the parent language that the rest evolved from. Linguistic Anthropologists try to reconstruct family trees of languages and connect their relationships over time.
How Many Different Language Families Are There?
There are 142 different language families all around the world. However, there are 6 major language families: Niger-Congo, Austronesian, Trans-New Guinea, Sino-Tibetan, Indo-European, and Afro-Asiatic. Here is a little information about each language family.
Niger-Congo
The Niger-Congo language family contains over 1500 languages found in sub-Saharan and southern Africa.

Austronesian
The Austronesian language family contains over 1200 languages found in places like China, New Zealand, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, Chile, and the United States.

Trans-New Guinea
The Trans-New Guinea language family contains over 470 languages found in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea.

Sino-Tibetan
The Sino-Tibetan language family contains over 450 languages found in China, India, Pakistan, and parts of Southeast Asia, including Thailand, Vietnam, and Myanmar.

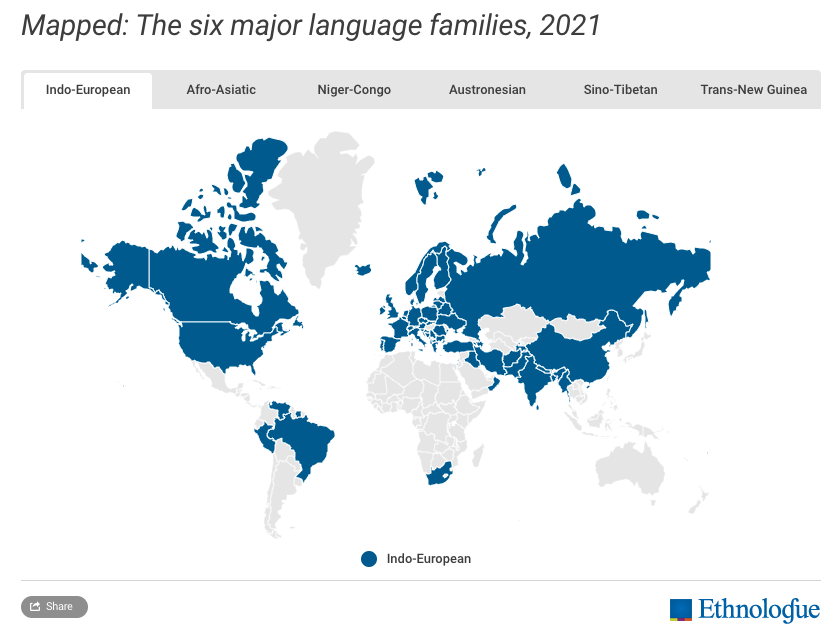
Indo-European
The Indo-European language family contains over 440 languages found in North America, parts of South America, Europe, Russia, and other places.
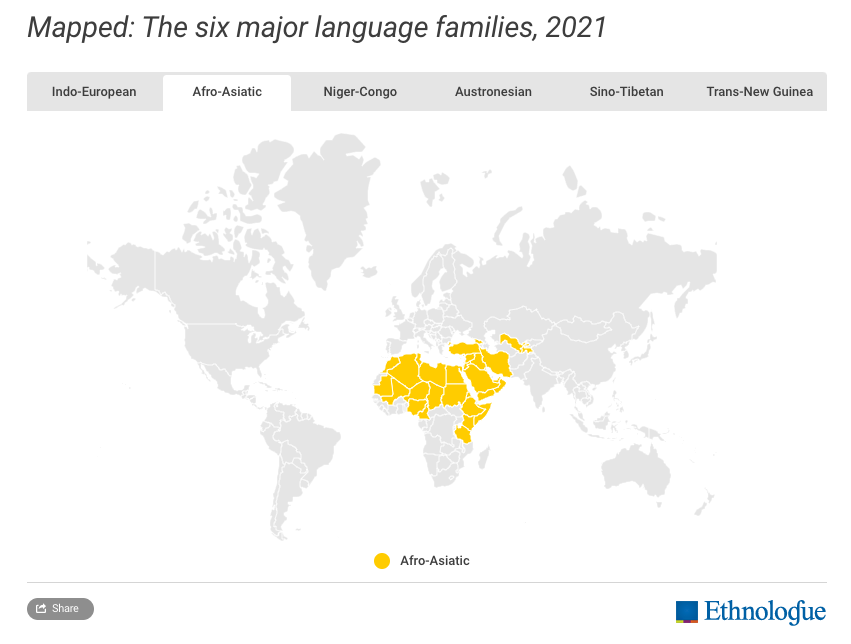
Afro-Asiatic
Finally, the Afro-Asiatic language family consists of over 350 languages found in northern Africa and the Middle East.
Is Every Language Part of a Language Family?
No! While most languages can be classified into language families, there are a few languages that are not related to any known language. These are called language isolates. Examples include the Basque language spoken in southwestern Europe, and the Ainu language, spoken on a northern Japanese island.
Learn More
Do you want to learn more about how languages are related? Check out the Ethnologue website’s article, “What are the Largest Language Families?”
And, check out the article, “All in the Language family: A Guide to the Language Families of the World.”
Also, be sure to check out the article, “A Language Family Tree-In Pictures” for more information on how languages are related.
Thanks for reading!
The post Linguistic Anthropology: How Are Languages Related? appeared first on Anthropology 4U.







