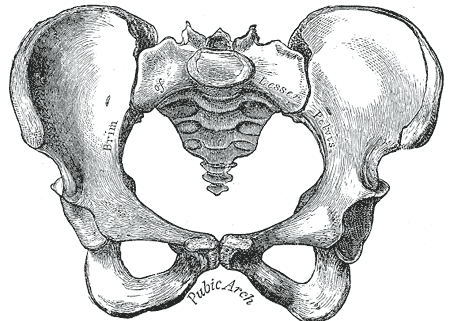
Helps in a forensic context for the biological profile. Population, and environmental stressors like mobility, and disease affect body size/shape. Can also be used to understand the sexual dimorphism of extinct hominins.Ecogeographical rules related to thermoregulation:Bergmann’s Rule (1847) If you have...
Helps in a forensic context for the biological profile.
Population, and environmental stressors like mobility, and disease affect body size/shape. Can also be used to understand the sexual dimorphism of extinct hominins.
Ecogeographical rules related to thermoregulation:
Bergmann’s Rule (1847) If you have a species that is variable, and spread out over a geographical area you will see a larger variance of those species. Relating to body mass; bigger in colder climates, smaller in warmer climates.
Allen’s Rule (1877) concerned with appendage’s. Shorter in colder climates, and longer in warmer climates.
Together they are Bergmann’s and Allen’s rules.
A great modern example is observed in the following populations:
Inuit, Shorter limbs, and rounder stocky body:

Image Source: Ansgar Walk. Traditional clothing; left: seal, right: caribou (Iglulik). Wikimedia Commons.
Maasai, Longer limbs, slender taller body:
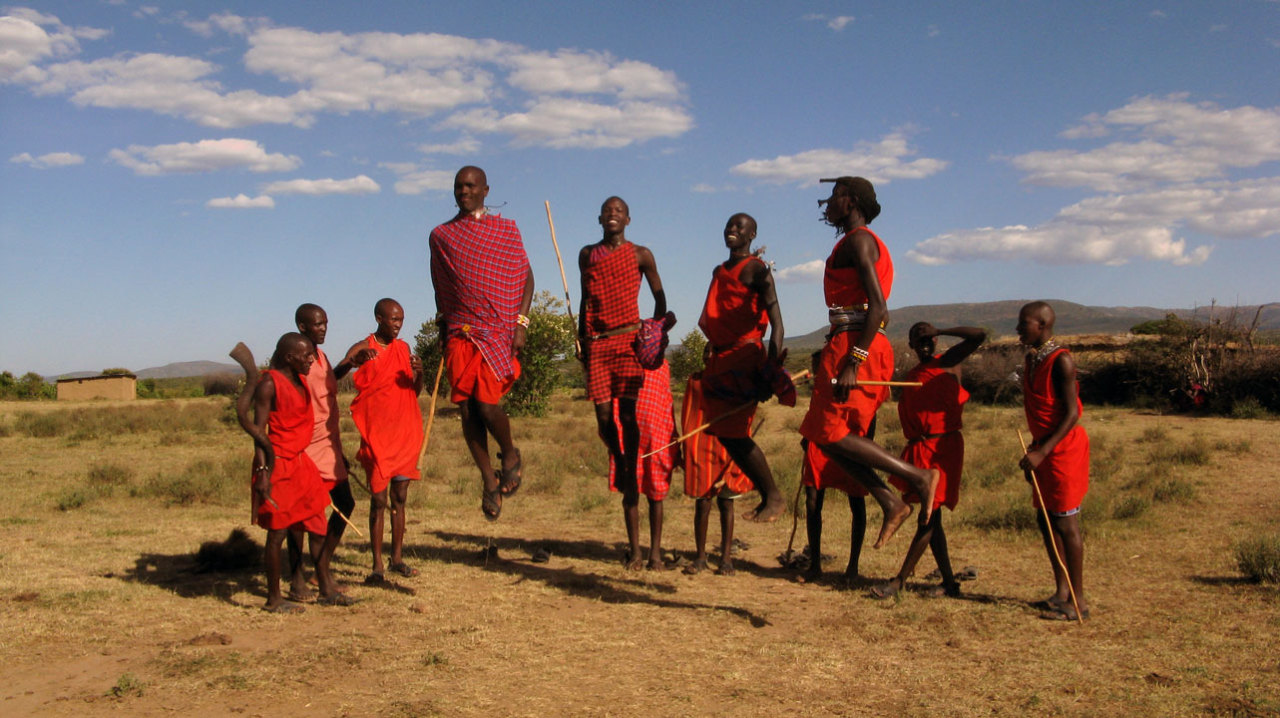

Image Source: Brutere. Maasai men performing traditional jumping dance (Adumu). Wikimedia Commons.
This is showing basic phenotypical adaptations to different climates, and how the environment can biologically change populations.
Note: Diet, nutrition, humidity, and variation (and many other variables) play a role in phenotype.