In the rapidly evolving landscape of Natural Language Processing, 2023 emerged as a pivotal year, witnessing groundbreaking research in the realm of Large Language Models (LLMs). The post The GenAI Frontier: 10 Transformative LLM Research Papers of 2023 from...
Generated with DALL-E 3
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Natural Language Processing, 2023 emerged as a pivotal year, witnessing groundbreaking research in the realm of Large Language Models (LLMs). These LLMs, characterized by their vast parameter sizes and impressive capabilities, played a central role in shaping the future of AI applications. This introduction provides a glimpse into the transformative research that unfolded in the field, where language models have been refined, scaled down, and even integrated with external tools to tackle a diverse range of tasks.�
If you�d like to skip around, here are the research papers we featured:
LLaMA by Meta AI LLaMA 2 by Meta AI GPT-4 by OpenAI Sparks of AGI by Microsoft BLIP-2 by Salesforce InstructBLIP by Salesforce PALM-E by Google PALM-2 by Google Toolformer by Meta AI Tree of Thoughts by Princeton University and Google DeepMindIf such research summaries are useful for you, subscribe to our AI mailing list to be alerted when we release new material.�
Top LLM Research Papers 2023
1. LLaMA by Meta AI
Summary�
The Meta AI team asserts that smaller models trained on more tokens are easier to retrain and fine-tune for specific product applications. Therefore, they introduced LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI), a collection of foundational language models with 7B to 65B parameters. LLaMA 33B and 65B were trained on 1.4 trillion tokens, while the smallest model, LLaMA 7B, was trained on one trillion tokens. They exclusively used publicly available datasets, without depending on proprietary or restricted data. The team also implemented key architectural enhancements and training speed optimization techniques. Consequently, LLaMA-13B outperformed GPT-3, being over 10 times smaller, and LLaMA-65B exhibited competitive performance with PaLM-540B.
Where to learn more about this research?
LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models (research paper) Introducing LLaMA: A foundational, 65-billion-parameter large language model (blog post)Where can you get implementation code?
The code implementation of the original LLaMA-1 model is available here on GitHub.2. LLaMA 2 by Meta AI
Summary�
LLaMA 2 is an enhanced version of its predecessor, trained on a new data mix, featuring a 40% larger pretraining corpus, doubled context length, and grouped-query attention. The LLaMA 2 series of models includes LLaMA 2 and LLaMA 2-Chat, optimized for dialogue, with sizes ranging from 7 to 70 billion parameters. These models exhibit superior performance in helpfulness and safety benchmarks compared to open-source counterparts and are comparable to some closed-source models. The development process involved rigorous safety measures, including safety-specific data annotation and red-teaming. The paper aims to contribute to the responsible development of LLMs by providing detailed descriptions of fine-tuning methodologies and safety improvements.
Where to learn more about this research?
Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models (research paper) Llama 2: open source, free for research and commercial use (blog post)Where can you get implementation code?
Meta AI released LLaMA 2 models to individuals, creators, researchers, and businesses of all sizes. You can access model weights and starting code for pretrained and fine-tuned LLaMA 2 language models through GitHub.3. GPT-4 by OpenAI
Summary�
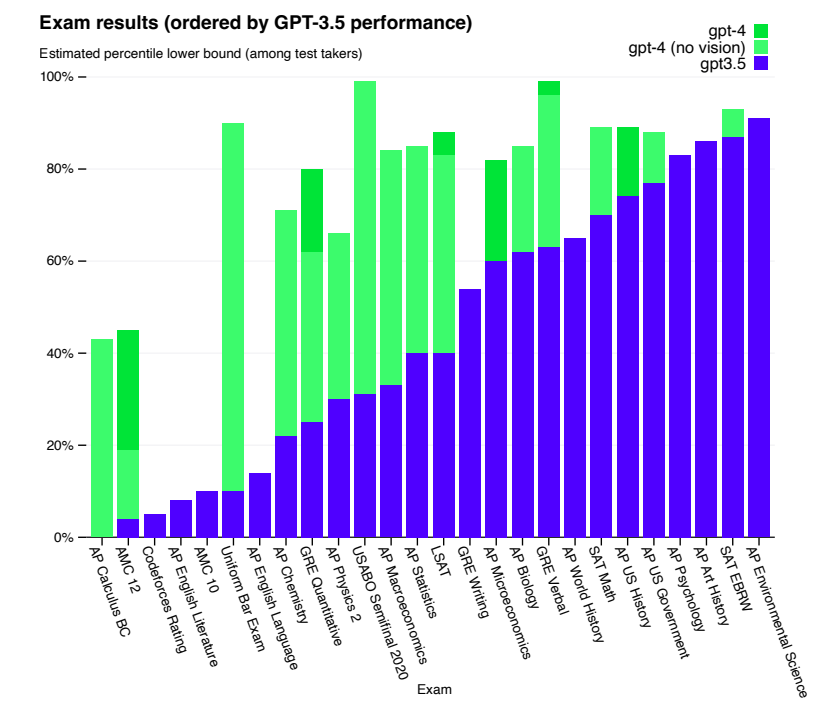
GPT-4 is a large-scale, multimodal model that accepts image and text inputs and generates text outputs. Due to competitive and safety concerns, specific details about the model�s architecture and training are withheld. In terms of performance, GPT-4 surpasses previous language models on traditional benchmarks and shows significant improvements in user intent understanding and safety properties. The model also achieves human-level performance on various exams, including a top 10% score on a simulated Uniform Bar Examination.
Where to learn more about this research?
GPT-4 Technical Report (research paper) GPT-4 (blog post)Where can you get implementation code?
Code implementation of GPT-4 is not available.4. Sparks of AGI by Microsoft
Summary
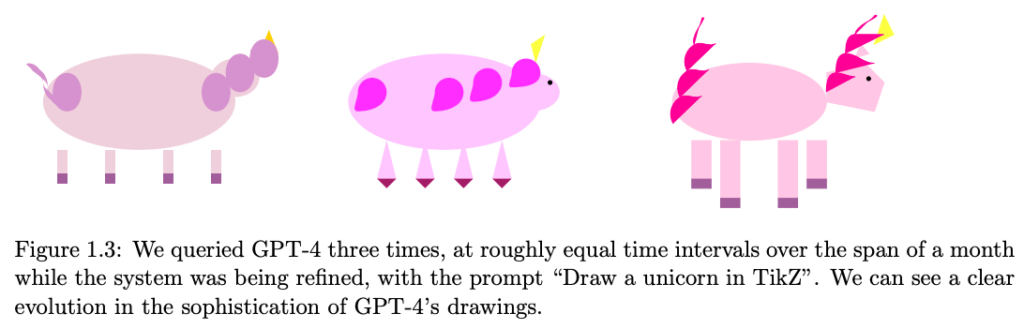
In this research paper, a team from Microsoft Research analyzes an early version of OpenAI�s GPT-4, which was still under active development at the time. The team argues that GPT-4 represents a new class of large language models, exhibiting more generalized intelligence compared to previous AI models. Their investigation reveals GPT-4�s expansive capabilities across various domains, including mathematics, coding, vision, medicine, law, and psychology. They highlight that GPT-4 can solve complex and novel tasks without specialized prompting, often achieving performance close to human level.�
The Microsoft team also emphasizes the potential of GPT-4 to be considered an early, albeit incomplete, form of artificial general intelligence (AGI). They focus on identifying GPT-4�s limitations and discuss the challenges in progressing towards more advanced and comprehensive AGI versions. This includes considering new paradigms beyond the current next-word prediction model.
Where to learn more about this research?
Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4 (research paper) Sparks of AGI: early experiments with GPT-4 (a talk by the paper�s first author S�bastien Bubeck)Where can you get implementation code?
Not applicable5. BLIP-2 by Salesforce
Summary�
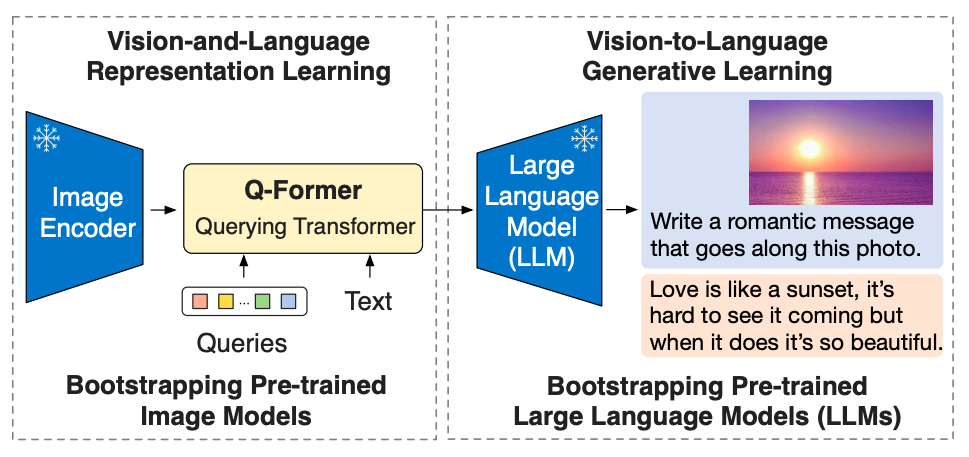
BLIP-2 is an efficient and generic pre-training framework for vision-and-language models, designed to circumvent the increasingly prohibitive cost of pre-training large-scale models. BLIP-2 leverages off-the-shelf frozen pre-trained image encoders and frozen large language models to bootstrap vision-language pre-training, incorporating a lightweight Querying Transformer pre-trained in two stages. The first stage initiates vision-language representation learning from a frozen image encoder, and the second stage propels vision-to-language generative learning from a frozen language model.�
Despite having significantly fewer trainable parameters, BLIP-2 outperforms state-of-the-art methods, surpassing DeepMind�s Flamingo80B by 8.7% on zero-shot VQAv2 with 54x fewer trainable parameters. The model also exhibits promising zero-shot image-to-text generation capabilities following natural language instructions.
Where to learn more about this research?
BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models (research paper) BLIP-2: Scalable Pre-training of Multimodal Foundation Models for the World�s First Open-source Multimodal Chatbot (blog post)Where can you get implementation code?
The official BLIP-2 implementation is available here on GitHub.6. InstructBLIP by Salesforce
Summary�
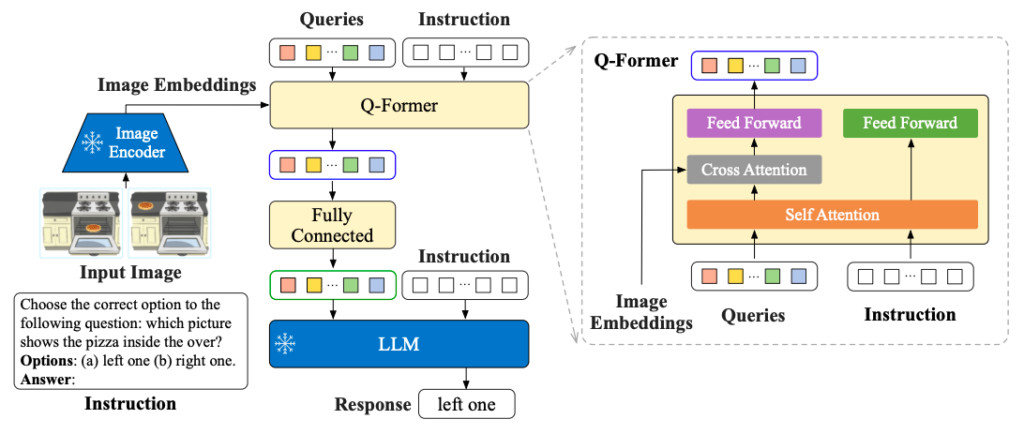
InstructBLIP is a novel framework for vision-language instruction tuning, enabling general-purpose models to process a wide range of visual tasks using natural language instructions. This study builds on the pre-trained BLIP-2 model, incorporating an image encoder, a large language model, and a Querying Transformer (Q-Former) to integrate the two. The instruction tuning involves fine-tuning the Q-Former while keeping the image encoder and LLM frozen. For comprehensive study and evaluation, the researchers transformed 26 datasets into instruction tuning format, using 13 datasets for instruction tuning and 13 for zero-shot evaluation. A key innovation is the instruction-aware visual feature extraction, allowing the model to extract relevant features based on given instructions.�
InstructBLIP models demonstrate state-of-the-art zero-shot performance across various vision-language tasks, significantly outperforming BLIP-2 and larger Flamingo models, as well as leading to state-of-the-art performance, when finetuned on individual downstream tasks (e.g., 90.7% accuracy on ScienceQA questions with image contexts).
Where to learn more about this research?
InstructBLIP: Towards General-purpose Vision-Language Models with Instruction Tuning (research paper)Where can you get implementation code?
The official InstructBLIP implementation is also available on GitHub.7. PALM-E by Google
Summary
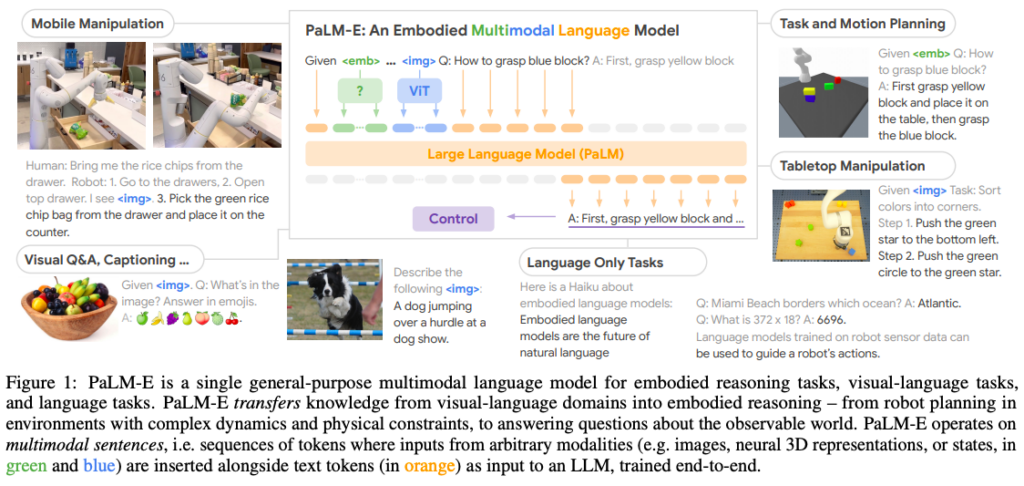
The research paper introduces PaLM-E, a novel approach to language models that bridges the gap between words and percepts in the real world by directly incorporating continuous sensor inputs. This embodied language model seamlessly integrates multi-modal sentences containing visual, continuous state estimation, and textual information. These inputs are trained end-to-end with a pre-trained LLM and applied to various embodied tasks, including sequential robotic manipulation planning, visual question answering, and captioning.
PaLM-E, particularly the largest model with 562B parameters, demonstrates remarkable performance on a wide range of tasks and modalities. Notably, it excels in embodied reasoning tasks, exhibits positive transfer from joint training across language, vision, and visual-language domains, and showcases state-of-the-art capabilities in OK-VQA benchmarking. Despite its focus on embodied reasoning, PaLM-E-562B also exhibits an array of capabilities, including zero-shot multimodal chain-of-thought reasoning, few-shot prompting, OCR-free math reasoning, and multi-image reasoning, despite being trained on only single-image examples.
Where to learn more about this research?
PaLM-E: An Embodied Multimodal Language Model (research paper) PaLM-E (demos) PaLM-E (blog post)Where can you get implementation code?
Code implementation of the PaLM-E model is not available.8. PALM-2 by Google
Summary
In May 2023, the Google team introduced PaLM 2, a successor to the original PaLM that exhibits enhanced multilingual capabilities, better reasoning skills, and greater computational efficiency. PaLM 2, based on a Transformer architecture, is trained using a mix of objectives and has been extensively evaluated on tasks involving English and other languages, as well as reasoning challenges.�
The findings show that PaLM 2 significantly outperforms its predecessor in terms of task performance across various model sizes, while also achieving faster and more efficient inference. PaLM 2�s robust reasoning abilities are highlighted by substantial improvements over the original PaLM in BIG-Bench and other reasoning tasks. The model also maintains stable performance in responsible AI evaluations and offers inference-time control over toxicity without compromising other capabilities or incurring extra overhead.
Where to learn more about this research?
PaLM 2 Technical Report (research paper) Introducing PaLM-2 (blog post) PaLM-2 (overview)Where can you get implementation code?
Code implementation of the PaLM-2 model is not available.9. Toolformer by Meta AI
Summary
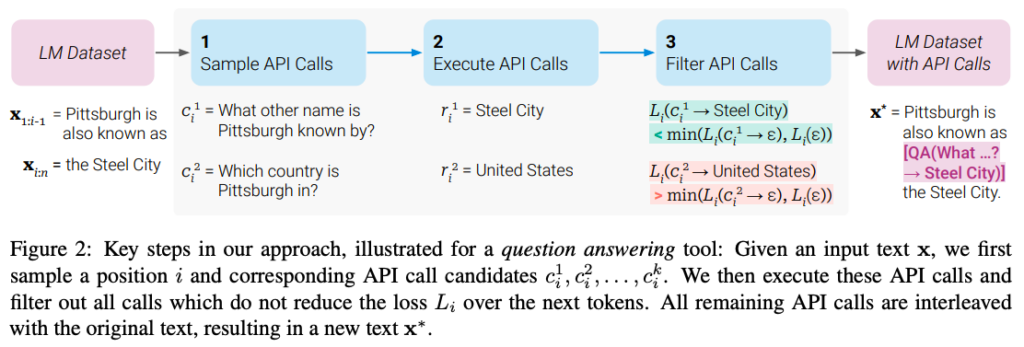
The research paper introduces Toolformer, a novel approach to enhance the capabilities of large language models (LMs) by enabling them to utilize external tools through simple APIs. While LMs excel at solving new tasks from limited examples or textual instructions, they often struggle with basic functions like arithmetic or factual lookup, where smaller models perform better. Toolformer bridges this gap by teaching LMs to autonomously determine which APIs to invoke, when to call them, what arguments to provide, and how to integrate the results into future token predictions. This learning process is self-supervised and requires only a small number of demonstrations for each API. Toolformer, based on a pretrained GPT-J with 6.7 billion parameters, significantly improves zero-shot performance across various downstream tasks, outperforming a much larger GPT-3 model and other baselines.
Where to learn more about this research?
Toolformer: Language Models Can Teach Themselves to Use Tools (research paper)Where can you get implementation code?
The open-source implementation of Toolformer is available on GitHub.10. Tree of Thoughts by Princeton University and Google DeepMind
Summary
The research paper introduces a groundbreaking framework for language model inference called Tree of Thoughts (ToT). LLMs have proven adept at solving tasks but are limited to token-level, left-to-right decision-making during inference. This hinders their performance in tasks requiring exploration, strategic lookahead, or pivotal initial decisions. ToT builds upon the Chain of Thought approach to prompting LLMs and enables exploration over coherent units of text called �thoughts.� These thoughts serve as intermediate steps in problem-solving, empowering LLMs to make deliberate decisions by considering multiple reasoning paths, self-evaluating choices, and making global decisions by looking ahead or backtracking when needed. The inspiration for ToT comes from �dual process� models in human decision-making, where fast, automatic decisions (System 1) are complemented by slower, deliberate decisions (System 2).
Empirical experiments demonstrate ToT�s effectiveness on challenging tasks such as Game of 24, Creative Writing, and Crosswords. As an example, in the Game of 24, where GPT-4 using chain-of-thought prompting managed to solve only 4% of the tasks, this approach achieved a remarkable success rate of 74%.
Where to learn more about this research?
Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models (research paper) Twitter thread by the paper�s first author Shunyu YaoWhere can you get implementation code?
The official code implementation of the paper is available on GitHub.As researchers continue to push the boundaries of what LLMs can achieve, the future of AI applications looks increasingly promising, offering solutions to complex challenges and enhancing human-AI collaboration. The journey of innovation in LLMs is far from over, and the world eagerly awaits the next wave of breakthroughs in the ever-expanding field of artificial intelligence.
Enjoy this article? Sign up for more AI research updates.
We�ll let you know when we release more summary articles like this one.
The post The GenAI Frontier: 10 Transformative LLM Research Papers of 2023 from LLaMA to GPT-4 appeared first on TOPBOTS.