A turbocharged petrol (gasoline) engine, often referred to simply as a "turbocharged engine," is an internal combustion engine that uses a turbocharger to increase its power and efficiency. Turbocharging is a technology commonly used in both petrol and diesel...
A turbocharged petrol (gasoline) engine, often referred to simply as a "turbocharged engine," is an internal combustion engine that uses a turbocharger to increase its power and efficiency. Turbocharging is a technology commonly used in both petrol and diesel engines to improve performance. Here's how it works:
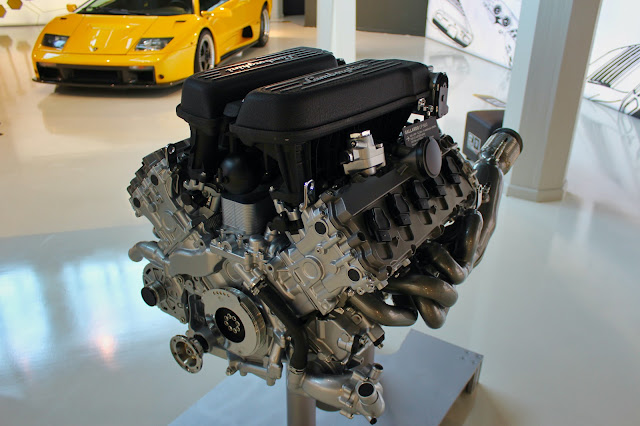
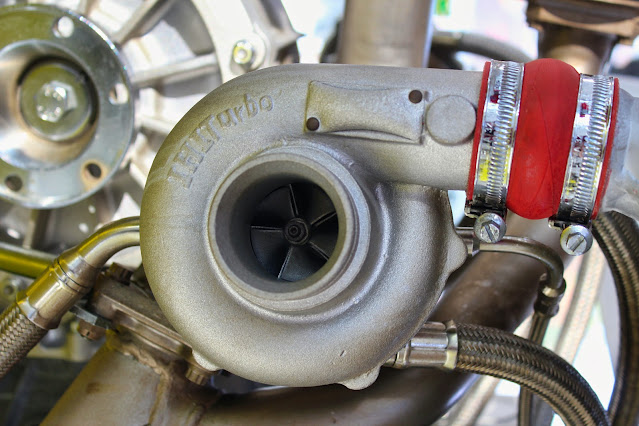
1. Turbocharger: A turbocharger is a device that consists of two main components - a turbine and a compressor - connected by a common shaft. It is typically mounted on the exhaust manifold of the engine. The turbine is placed in the path of exhaust gases exiting the engine, and the compressor is positioned in the engine's air intake system.
2. Exhaust Gas Energy: As the engine burns petrol (gasoline), it produces exhaust gases that exit through the exhaust manifold. These hot and high-velocity exhaust gases are directed through the turbine of the turbocharger.
3. Turbine Operation: The exhaust gases passing through the turbine cause it to spin. Since the turbine and compressor are connected, the spinning turbine also drives the compressor.
4. Compressor Operation: The spinning compressor draws in and compresses fresh air from the atmosphere. This compressed air is then forced into the engine's intake manifold, where it mixes with fuel before entering the combustion chambers.
5. Increased Air Supply: By compressing the incoming air, the engine can ingest a greater volume of air, which means it can burn more fuel and produce more power. This process is often referred to as forced induction because it forces more air into the engine than it could naturally aspirate (draw in) on its own.
Benefits of a Turbocharged Petrol Engine:
1. Increased Power: Turbocharging can significantly boost an engine's power output. This is especially useful in smaller engines where manufacturers want to achieve higher power levels without increasing engine size.
2. Improved Efficiency: Turbochargers can help improve fuel efficiency by allowing smaller engines to produce power levels typically associated with larger engines. This can lead to better fuel economy when driven at lower power levels.
3. Reduced Emissions: A turbocharged engine can deliver better power-to-emissions ratios, helping to reduce emissions and meet stricter environmental regulations.
4. Torque: Turbocharged engines often produce more low-end torque, which can enhance acceleration and overall driving performance.
However, there are some potential downsides to turbocharged petrol engines, such as increased complexity, potential for turbo lag (a delay in power delivery), and the need for more maintenance due to higher stresses on engine components.
Many modern petrol engines, especially in performance-oriented and compact vehicles, use turbocharging technology to balance power and efficiency. The size and design of the turbocharger, as well as the engine management system, are crucial factors in achieving the desired balance between power, efficiency, and drivability in a turbocharged petrol engine.