Pilot workload refers to the mental and physical demands placed on a pilot during flight. It encompasses everything from monitoring The post Understanding Pilot Workload: Keeping Pilots Focused and Safe appeared first on aviation related posts, aviation pioneers and...
Pilot workload refers to the mental and physical demands placed on a pilot during flight. It encompasses everything from monitoring instruments to making decisions and responding to emergencies. Managing this workload is crucial for safe and efficient flying.
Why Pilot Workload Matters:
Reduced Fatigue: High workload can lead to fatigue, impacting performance and decision-making. Improved Situational Awareness: When workload is manageable, pilots can better focus on their surroundings and anticipate potential problems. Enhanced Safety: Managing distractions and maintaining situational awareness minimizes errors and promotes safety.Factors Affecting Workload:
Flight Phase: Takeoff and landing require more attention and effort, increasing workload. Weather Conditions: Turbulence, poor visibility, and other adverse weather can significantly increase workload. Aircraft Malfunctions: Unexpected problems require immediate attention and troubleshooting, raising workload. Crew Coordination: Effective communication and teamwork help distribute workload and manage critical situations.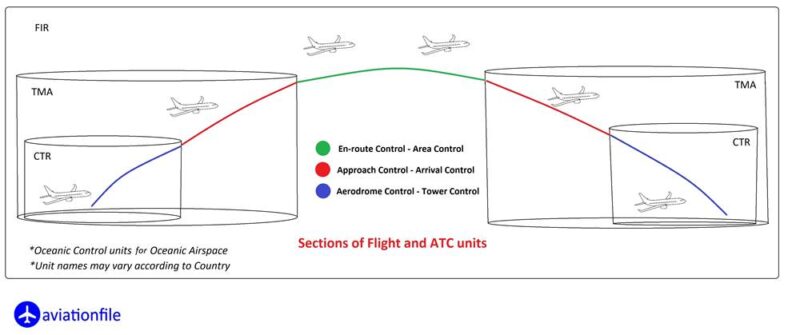 Sections of Flight
Sections of Flight
Strategies for Managing Workload:
Automation: Utilizing autopilot and other automated systems reduces manual tasks and frees up mental resources. Crew Resource Management (CRM): Collaborative decision-making and clear communication optimize crew performance and share workload. Training and Proficiency: Regularly practicing various scenarios and emergency procedures builds confidence and reduces stress during real events.Monitoring and Measuring Workload:
Subjective Assessments: Pilots can self-report their workload through various scales and questionnaires. Physiological Measures: Tracking heart rate, eye movement, and brain activity can offer objective assessments. Performance Data: Analyzing flight data and performance metrics can identify areas where workload may be excessive.Conclusion:
Managing pilot workload is a critical aspect of aviation safety. By understanding the factors that affect workload and implementing effective strategies, we can ensure that pilots remain focused, alert, and able to perform their duties effectively.
References:
P Workload | SKYbrary Aviation Safety: https://skybrary.aero/articles/pilot-workload P WORKLOAD AND FATIGUE: A CRITICAL SURVEY OF CONCEPTS AND ASSESSMENT TECHNIQUES: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/19770004731/downloads/19770004731.pdf Measurement of Pilot’s Workload During NDB and ILS Approaches – ScienceDirect: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352146521008528 Pilot workload and human factors: the shift from manager to decision-maker: https://onboard.thalesgroup.com/pilot-workload-human-factors-shift-manager-decision-maker/ Objective Measures of Pilot Workload – DTIC: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/citations/AD1088654The post Understanding Pilot Workload: Keeping Pilots Focused and Safe appeared first on aviation related posts, aviation pioneers and aviation accidents.