The Buddhist concept of emptiness refers to the idea that all things lack intrinsic or inherent existence. It is a way of understanding the nature of reality and the way in which things come into being. By recognising the...
The Buddhist concept of emptiness refers to the idea that all things lack intrinsic or inherent existence. It is a way of understanding the nature of reality and the way in which things come into being. By recognising the emptiness of all things, we can let go of our attachment to fixed identities and concepts, leading to greater freedom and compassion.
The concept of emptiness is probably the most difficult to understand in Buddhism. It is also one of the most misunderstood, and so in this article I will explore the concept of emptiness and its practical implications for our lives.
What is emptiness?
The concept of emptiness is a central Buddhist teaching. At its core, emptiness refers to the idea that all things lack intrinsic or inherent existence. This means that everything in the world, and that includes ourselves, is empty of any unchanging, permanent essence. If things had their own inherent nature, it would mean they are permanent and have an unchanging nature. It would also mean they arose without a cause and are completely indestructible.
It is often misunderstood as nihilistic or negative. However, emptiness does not mean that things do not exist or that the world is meaningless. Rather, it is a way of understanding the nature of reality and the way in which things come into being.
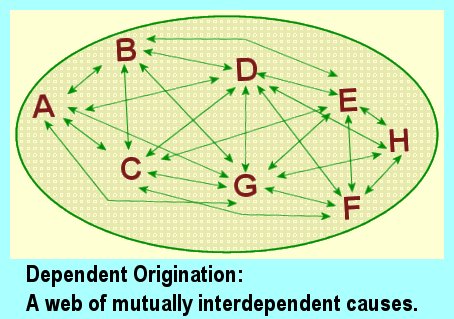
If we are trying to understand emptiness, it is helpful to first reflect on the concept of dependent origination. According to this concept, everything in the world arises in dependence upon other things. Nothing exists independently or in isolation. All things are interconnected and interdependent. This concept is a fundamental teaching in Buddhism that explains the nature of existence and the causes of suffering.
Buddha taught that all things are conditioned by other things, and nothing exists independently or in isolation. Every phenomenon arises due to a complex web of causes and conditions, which themselves arise due to other causes and conditions. This chain of causation is known as the �twelve links of dependent origination.�
The twelve links begin with ignorance, which leads to actions and choices, which in turn lead to consciousness, and so on through birth, old age, and death. Each link in the chain is dependent on the previous link, and the entire chain perpetuates the cycle of existence.
The Buddha taught that being delusional about the way life really is causes us to suffer, and that by understanding the chain of dependent origination, one can break free from the cycle of suffering and attain liberation or freedom from a deluded mind. By understanding the causes and conditions that lead to suffering, one can begin to uproot the underlying delusion and cultivate wisdom, which leads to the alleviation of suffering.
In a nutshell, dependent origination teaches that everything is impermanent, constantly changing, and interconnected. It invites us to investigate the nature of reality and to see things as they truly are, rather than as we imagine them to be. Investigating dependent origination helps us to develop an awareness of the causes and conditions that lead to suffering, and cultivate the wisdom necessary to attain ultimate freedom, which is not an external freedom but a freedom from the delusional projections of the mind.
(You can read more about this topic here � https://yesherabgye.com/the-twelve-links-of-dependent-arising)
So, emptiness is the recognition that this interconnectedness and interdependence means that everything lacks inherent existence. All things are dependent upon other things for their existence and identity. This means that everything is impermanent, constantly changing, and ultimately insubstantial.
Emptiness can also lead to greater compassion and interconnectedness. When we recognise the emptiness of all things, we can see that everything is interconnected and interdependent. This can lead to a greater sense of compassion for others, as we recognise that their experiences are also impermanent and constantly changing.
Practical examples of emptiness
Understanding emptiness is not just an intellectual exercise, so let�s consider some practical examples. Take a table, for instance. We might think of a table as a solid, stable object with a fixed identity. However, when we examine the table more closely, we see that it is made up of various parts, such as legs, a top, and screws or nails. These parts are themselves made up of smaller parts, and so on.

Furthermore, the table is dependent upon other things for its existence. It is made from wood, which comes from trees that rely on sunlight, water, and soil for their growth. The table was also created by a carpenter, who used tools and materials that were themselves created by other people and processes.
In other words, the table is not a fixed, permanent object. It is a temporary arrangement of parts that is dependent upon other things for its existence. The table is empty of intrinsic nature.
Emptiness can also be applied to a car by recognising that it is composed of many different parts, such as the engine, wheels, and body. These parts are not inherently a car in and of themselves, but rather they come together to create the appearance of a car. In other words, the car is empty of car-ness, or a self-nature that makes it inherently a car.
Furthermore, the car is also impermanent and subject to change. It is constantly undergoing wear and tear, and eventually, it will break down and cease to exist as a car.
By recognising the emptiness of a car, we can begin to see it as simply a temporary phenomenon that arises due to various causes and conditions.
So, understanding that all phenomena are empty, or have no intrinsic nature, can help us let go of our attachment to material possessions and develop a greater sense of equanimity.�
Benefits of understanding emptiness
Understanding the Buddhist concept of emptiness can offer a range of benefits in our lives, both on a personal and social level. Here are some of the main benefits:
1. Freedom from suffering: According to Buddhist teachings, the root of suffering is attachment to things that are impermanent and constantly changing. By recognising the emptiness of all things, we can let go of our attachment to fixed identities and concepts. This can lead to greater freedom and a reduction in our suffering.
2. Compassion and interconnectedness: When we recognise the emptiness of all things, we can see that everything is interconnected and interdependent. This can lead to a greater sense of compassion for others, as we recognise that their experiences are also impermanent and constantly changing.
3. Wisdom and insight: The recognition of emptiness can lead to greater wisdom and insight into the nature of reality. It can help us to see things as they really are, rather than being caught up in our own limited perceptions and concepts.
4. Reduced conflict: Many of the conflicts in our world arise from a sense of fixed identities and concepts, such as nationalistic or religious identities. By recognising the emptiness of these identities, we can reduce our attachment to them and become more open to others.
5. Environmental awareness: The recognition of emptiness can also lead to greater awareness of our interconnectedness with the natural world. By identifying that everything is interdependent and impermanent, we can become more mindful of our impact on the environment and work towards greater sustainability.
So, understanding the concept of emptiness can offer a range of benefits in our lives, including greater freedom from suffering, compassion for others, wisdom and insight, reduced conflict, and environmental awareness. It can help us to see things as they really are and become more mindful and compassionate beings.
If you would like to become a supporter of Buddhism Guides work, such as podcasts, blogs, videos and guided meditation practices, please visit�here. You can support for as little as $2 a month.